- Baby at 14 weeks pregnant
- Pregnant woman at 14 weeks of pregnancy
- Prenatal checkup at 14 weeks of pregnancy
- Characteristics of Down syndrome revealed by ultrasound at 14th week of pregnancy
- NIPT (New Prenatal Test) that detects Down syndrome from 6 weeks of pregnancy
- まとめ
The state of the baby in the womb
At 14 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta is nearing completion and begins to prepare to receive nutrients from the umbilical cord. This is the time when the fetus’s organs, muscles, neck, limbs, and other parts of the body begin to develop. Although the subcutaneous tissue (fat) has not yet formed, the skin gradually thickens and downy hair begins to grow. The baby’s heart also begins to beat steadily, with a heart rate of approximately 150 beats per minute. This is more than double the mother’s heart rate (approximately 60 to 70 beats per minute).
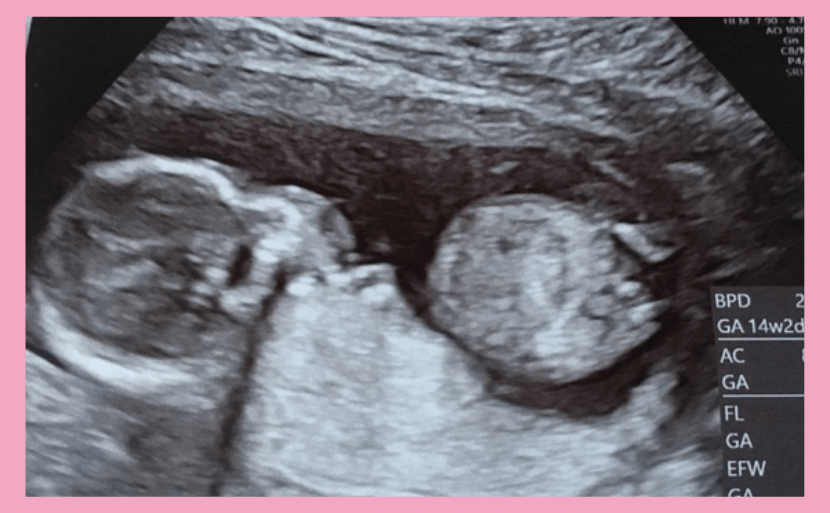
At 14 weeks pregnant, the baby’s size is approximately 90mm in crown-rump length (CRL) and weight is about 20-25g. An abdominal ultrasound scan may show the baby’s stomach bubble and urine accumulating in the bladder. At 14 weeks pregnant, the baby turns over in the amniotic fluid and begins to move its arms and legs actively. However, it is not until the 18th week of pregnancy that you can feel fetal movement.

Ultrasound photo taken at 14 weeks of pregnancy.
Determining the baby’s gender by ultrasound
Sex differentiation of a fetus occurs at the time of fertilization. The chromosomes that determine gender (sex chromosomes) are the “X chromosome” and the “Y chromosome,” so if a man is XY, then he will have XX chromosomes, and if a woman is XX chromosomes. If an abnormality occurs in the sex chromosomes, it will result in aneuploidy, such as one X or XXY, which often leads to congenital disorders.
By the time you reach 14 weeks of pregnancy, your baby’s external genitalia is almost fully formed. However, it is generally not until the 18th week of pregnancy that you can determine your baby’s gender with an ultrasound, and even then, it can be difficult to determine the gender with certainty due to factors such as the position of your baby’s body.
Depending on the medical institution, the gender determined by the ultrasound examination during the prenatal checkup may not be communicated to the pregnant woman. If you are a pregnant woman who wants to know the gender of the baby before giving birth, check in advance whether you can be told the gender at the ultrasound examination.
14 weeks pregnant woman
Maternal condition at 14 weeks of pregnancy
At 14 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta is nearing completion and morning sickness will subside. This is generally considered to be the time when you are approaching the “stable period” when the risk of miscarriage is low.
During the 14th week of pregnancy, your physical condition will be more stable than during the early stages of pregnancy, so it is important to have a balanced diet and exercise moderately. However, as the baby grows and the uterus gets larger, many pregnant women suffer from frequent urination and urinary incontinence, and refrain from exercising or going out.
During the 14th week of pregnancy, once the peak of morning sickness has passed, it’s a good idea to take a walk around the neighborhood or do some light stretching indoors to change your mood and improve blood circulation.
In addition, since developing pregnancy gingivitis can lead to premature birth, it is also important to have a dental checkup at a dental clinic.
Common problems that can occur during the 14th week of pregnancy and things to be aware of
Beware of iron deficiency anemia
One of the problems that can easily occur during pregnancy is iron deficiency anemia. Even before pregnancy, one in five modern women suffer from iron deficiency anemia, and they tend to be chronically deficient in iron. In addition, twice as much iron is needed to produce red blood cells for the baby, and it is said that about 95% of anemia during pregnancy is due to iron deficiency.
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when the body is unable to produce hemoglobin, which is contained in red blood cells, due to a lack of iron in the body. Hemoglobin plays a role in transporting oxygen in the body, and iron deficiency often causes shortness of breath, palpitations, headaches, dizziness, and fatigue when exercising.
Effects of iron deficiency anemia on the fetus
Iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women impairs the normal growth and development of the fetus. In particular, a sufficient supply of oxygen is necessary for brain development. To prevent oxygen deficiency in the baby, be sure to eat a well-balanced diet and take in an appropriate amount of iron.
Anemia in pregnant women can also be caused by a lack of folic acid, not just iron. Folic acid deficiency anemia can cause congenital abnormalities in the fetus’s brain and spinal cord, so care must be taken.
Both iron deficiency anemia and folic acid deficiency anemia can be diagnosed through a blood test during a prenatal checkup. Follow your doctor’s instructions and take iron supplements and folic acid supplements.
Risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension and gestational diabetes
In the early stages of pregnancy, many pregnant women lose their appetite due to morning sickness, while others eat too many calories due to morning sickness. Also, at the 14th week of pregnancy, when morning sickness subsides, many women find that their appetite continues and they end up gaining weight.
Rapid weight gain during pregnancy is said to increase the risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension and gestational diabetes. Pregnancy-induced hypertension reduces blood flow, resulting in insufficient nutrition and oxygen reaching the fetus, leading to growth retardation. Caution is required as this increases the risk of low birth weight babies weighing less than 2500g, premature birth, and stillbirth. Gestational diabetes also supplies the fetus with excess sugar, which can lead to organ enlargement and large babies weighing over 4000g.
The 14th week of pregnancy is when morning sickness subsides and appetite returns. However, for the sake of your baby’s health, you should still try to eat an appropriate amount of nutritious, balanced food.
Risk of miscarriage at 14 weeks pregnant
At 14 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta stabilizes and the risk of miscarriage decreases. Morning sickness subsides, so many pregnant women resume work and exercise that they had refrained from during the early stages of pregnancy.
Miscarriages in the early stages of pregnancy are often caused by chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. On the other hand, miscarriages after the 12th week of pregnancy are said to be caused by the mother’s body as well. For these reasons, even at 14 weeks of pregnancy, when the pregnancy is approaching the stable period, the risk of miscarriage, such as threatened miscarriage, is never zero.
Moderate exercise is necessary, but be careful not to move or work too much. If you experience any abnormalities such as abdominal pain or bleeding, be sure to see a doctor immediately.

Prenatal checkup at 14 weeks
Up until the 12th week of pregnancy, a transvaginal ultrasound is used, and after that, a transabdominal ultrasound is used. Even if you are now at 14 weeks of pregnancy and your physical condition has stabilized, it is important not to be overconfident about your health and that of your baby, and to continue to have prenatal checkups at the scheduled times.
Main examination contents of prenatal checkup
| Blood pressure measurement | Tests to check for abnormalities such as pregnancy hypertension syndrome |
|---|---|
| Weight measurement | Tests for gestational hypertension syndrome and gestational diabetes based on weight changes |
| Blood test Tests | Tests to check for abnormalities such as anemia and gestational diabetes. |
| Urine test | Early detection of gestational hypertension and gestational diabetes. Tests for |
| Uterine fundus measurement | Test to check for abnormalities in the uterus, fetal size, and amniotic fluid volume |
| Transabdominal echo | Ultrasound fetal measurement Estimated fetal weight, morphological abnormalities, condition of umbilical cord and placenta, heart Testing of movements, body movements, amniotic fluid volume, etc. |
| Fetal Doppler method (fetal heart sounds) | Fetal heart rate and heart rhythm Check for heart disease and fetal health status |
Characteristics of Down Syndrome Detected by Ultrasound at 14 Weeks of Pregnancy
Ultrasound examinations during prenatal checkups are considered one type of prenatal diagnosis. At 14 weeks of pregnancy, ultrasound can be used to evaluate fetal morphological abnormalities and Down syndrome (trisomy 21) .
You can also tell the gender of the fetus from the shape of the external genitalia. However, gender determination by ultrasound is not a definitive test. Some medical institutions do not allow gender determination by ultrasound, so it is a good idea to check in advance.
The main characteristics that may suggest Down syndrome (trisomy 21) through ultrasound are the size of the head, swelling at the back of the neck, height of the nasal bone, and length of the limbs. However, ultrasound is not a definitive test for Down syndrome, but rather a screening test to evaluate the risk of Down syndrome .
In addition, there are many chromosomal abnormalities that cannot be evaluated by ultrasound alone, so in order to find out the risk of other chromosomal abnormalities, it is necessary to consider NIPT (non-invasive prenatal testing) .
NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) – Detecting Down Syndrome from 6 weeks of pregnancy
Ultrasound examinations performed during prenatal checkups are an excellent form of prenatal diagnosis for evaluating fetal morphological abnormalities. However, only a limited number of congenital diseases can be detected by ultrasound, making it difficult to evaluate all chromosomal abnormalities. On the other hand, NIPT (non-invasive prenatal testing) makes it possible to evaluate the risk of chromosomal abnormalities for all chromosomes in a baby.

What is NIPT (New Prenatal Testing)?
NIPT ( non-invasive prenatal testing) is a prenatal test also known as non-invasive prenatal genetic testing. As the word “non-invasive” suggests, there is no direct invasion (damage) to the fetus, and it is a screening test that assesses the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the baby using only maternal blood. NIPT (non-invasive prenatal testing) is considered to be a highly accurate test with a sensitivity and specificity of 99.9% for Down syndrome.
Summary
The biggest concern for pregnant women and their families is the health of their precious baby. “When can I start testing for Down syndrome ?” “Can I get tested up until the end of my pregnancy?” “What if the NIPT (non-invasive prenatal testing) test comes back positive for Down syndrome ?” There are endless worries during pregnancy, including miscarriage and premature birth.
NIPT (new type prenatal testing) can be performed from the sixth week of pregnancy. Knowing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus early in pregnancy can help protect not only the baby, but also the mother from health risks.
NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) by Hiro Clinic NIPT allows testing of all chromosomes and sex chromosomes of the baby. We also perform tests for Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) , which is said to have the highest incidence rate. If you have any questions about NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) or chromosomal abnormalities, please contact Hiro Clinic NIPT . Doctors and staff who are well versed in NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) will provide you with thorough support.
【References】
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare – For a healthy pregnancy and childbirth
Article Editorial Supervisor

Dr Hiroshi Oka
NIPT specialist clinic, MD
Graduated from Keio University, School of Medicine
 中文
中文