Introduction
It is known that approximately 10% of maternal blood contains DNA derived from the fetus that has flowed from the placenta. NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) is a test that detects the fetal DNA contained in the mother’s blood. This is a test to check for chromosomal abnormalities based on the amount of NIPT (New Prenatal Test) can be tested using the mother’s blood, so there is no effect on the fetus. It is a very useful test as there is no risk of miscarriage.
In the NIPT (New Prenatal Diagnostic Test) test, 21 It is possible to determine with very high accuracy whether a fetus has the three chromosomal abnormalities and sex chromosome abnormalities: trisomy (Down syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome). Masu.
However, NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) also has its limitations. A false negative is when a person who originally tested positive gets a negative result, and conversely, a false positive is when a person who should have tested negative gets a positive result. Is called. NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) can also cause false positives and false negatives. It is said that there are maternal chromosomal abnormalities, fetal mosaicism, and placental mosaicism. Due to mosaicism derived from the placenta, tests may show that the fetus has a chromosomal abnormality even though the chromosomes are normal.NIPT (New Prenatal Diagnostic Testing) is said to be a future challenge.

What is mosaic?
Now, let’s explain what a mosaic is. This refers to a situation where each cell in the body has a different number of chromosomes. For example, in Down syndrome mosaicism, cells with trisomy 21 and cells without trisomy 21 coexist at a certain ratio.
We will also briefly explain chromosomes to further understand mosaicism. Generally, all our cells have the same number of chromosomes. Unless there are chromosomal abnormalities, our cells contain two of each of the 22 autosomes, one X chromosome and one Y chromosome for men, and two X chromosomes for women. The X and Y chromosomes are called sex chromosomes, and 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes, a total of 46 chromosomes, are the number of chromosomes that our cells normally have.
NIPT (New Prenatal Diagnosis) can test for three chromosomal abnormalities in cells with The number of chromosomes is not 46. For example, in Down syndrome, the number of chromosome 21 increases from two to three, resulting in a total of 47 due to a chromosomal abnormality called trisomy.
The normal condition of two chromosomes is called disomy, when one chromosome is missing, it is called monosomy, and when there are four chromosomes, it is called tetrasomy.
Even if there is an abnormality in the number of chromosomes, when cell division occurs, one cell will divide into two identical cells. The number of chromosomes in a cell does not change before and after division. Therefore, people with an abnormality in the number of chromosomes generally have the same number of chromosomes in their body cells.
Mosaic mechanism
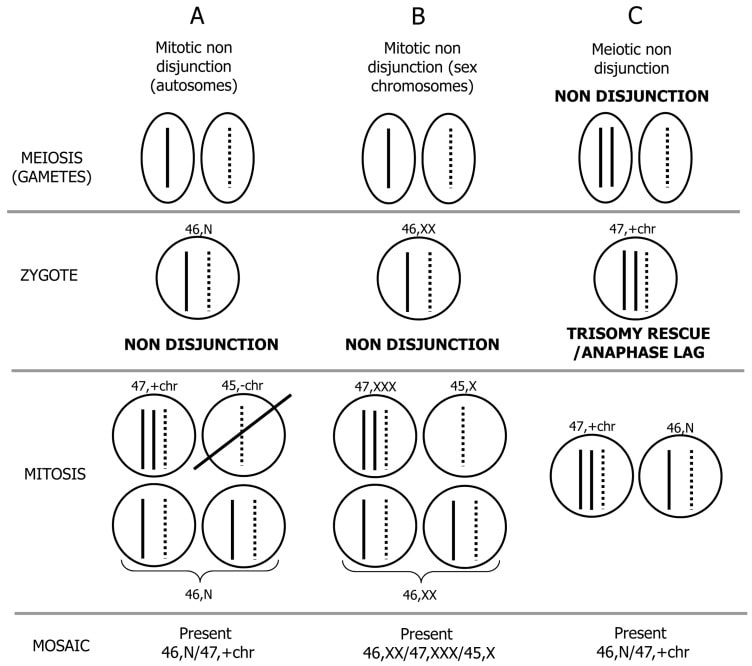
Mosaics can be broadly divided into two types: fetal mosaics and placental mosaics. The mechanism by which mosaic occurs can be broadly divided into three types, as shown in the diagram below.
Autosomal nondisjunction during cell division
The first is when autosomes do not divide properly during cell division. The mechanism shown in A shown in the figure below is that an originally normal sperm and egg are fertilized, and when the fertilized egg undergoes somatic cell division, an abnormality occurs when the autosomes do not separate, resulting in cells with trisomy and cells with monosomy. will occur. Cells with monosomy are often selected for selection, so cells with 46 chromosomes and cells with 47 chromosomes coexist. If chromosome 21 causes trisomy due to non-disjunction, it results in mosaic Down syndrome.
Sex chromosome non-disjunction during cell division
B shows how abnormal sex chromosome segregation occurs during cell division. When a woman’s two X chromosomes cannot separate properly into two cells during division, there are two types of cells: normal cells with two X chromosomes and monosomy cells with only one X chromosome. The result is a mosaic of trisomy cells that have three X chromosomes. Klinefelter syndrome is a disease of XXY males who have many X chromosomes, and it is said that they may have a mosaic pattern with different numbers of X chromosomes.
Parental chromosomal abnormalities
In the case of C, the chromosomes cannot separate into two cells during meiosis when the mother produces eggs, and the sex cell is fertilized with two chromosomes. represents. When fertilized, there are three chromosomes in total, including those from the father. As the three chromosomes undergo repeated cell division, a phenomenon called trisomy rescue occurs, in which excess chromosomes are eliminated from the cell.
Quote:Chromosomal Mosaicism in Human Feto-Placental Development: Implications for Prenatal Diagnosis
Example of false positive NIPT due to mosaic
It was reported in Japan that the result of NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) was caused by mosaic. Let me introduce one case that resulted in a false positive result.
This is a case of a 39-year-old primiparous woman. Because this patient gave birth at an older age, she underwent NIPT (a new type of prenatal Diagnosis)I took a test. The test results were positive for trisomy 18, but ultrasound and amniocentesis after 19 weeks revealed no chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. This test result was ultimately a false positive for NIPT (New Prenatal Testing) for trisomy 18. It was discovered at 21 weeks of pregnancy that there were no abnormalities in the fetal chromosomes. After delivery, it was discovered that the cause of the false positive result was placental mosaicism.
Placental mosaic isThis is a type of mosaicism in which mosaicism occurs only in the placenta, although the fetus does not have any chromosomal abnormalities.NIPT (New Prenatal Diagnosis))The DNA used in this test comes from both the fetus and the placenta’s cells called villi, so if there is a chromosomal abnormality in the placenta, a false positive result will appear.
In this case, a healthy newborn was finally delivered at 39 weeks. However, it has been reported that false positive results due to retesting and mosaicism delayed a definitive diagnosis, causing psychological stress to pregnant women.
What happens when it becomes a mosaic?
So what happens when you have a mosaic?
Mosaicism means that cells with a chromosomal abnormality and cells with a normal number of chromosomes coexist. It is said that the symptoms of mosaicism tend to be mild compared to the complete type, that is, cells with all chromosomal abnormalities.
However, if it is mosaic, it cannot necessarily be determined that the symptoms are mild or severe. This is because the symptoms of mosaic chromosomal abnormalities vary depending on the distribution of abnormal cells in specific tissues.
Mosaic Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality called trisomy 21, in which there is one extra chromosome 21. Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal abnormality, and is said to occur in 1 in 600 to 800 births. among themThe incidence of mosaic Down syndrome is approximately 2%.It is said that.
Symptoms include heart disease and congenital abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract, as well as decreased muscle tone. Another characteristic of Down syndrome is that it has a characteristic facial shape, such as a small head, flat face, slanted eyes, and a low nose.
Children with Down syndrome often have delays in intellectual development. Intelligence quotient (IQ) varies widely but is lower than that of normal children. on the other hand,Mosaic Down syndrome has a higher IQ than full Down syndromeThere is also a report that. I would like to introduce a study that investigated mosaic Down syndrome and IQ.
Study on IQ of Mosaic Down syndrome
I would like to introduce a study published in 1991 in the American Journal on Mental Retardation that examined the IQ of 30 children with Down syndrome and 30 children with Down syndrome mosaic.
We measured the IQ of each group of children with Down syndrome between the ages of 2 and 18. The average IQ of the group without the mosaic was 52, while the average of the group with the mosaic was 64. On average, those in the mosaic group had higher IQs.
The group with the mosaic had higher language ability and ability to express themselves through drawing than the group without the mosaic. On the other hand, we also found that the ability to handle numerical concepts is an issue for children with Mosaic Down syndrome. Thus, the researchers concluded that the intellectual development of children with mosaic Down syndrome follows a unique pattern compared to those with complete Down syndrome.
Mosaic Patou syndrome
Patau syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality caused by full-length or partial duplication of chromosome 13, resulting in trisomy of chromosome 13.
It is said to occur in 1 in 10,000 to 20,000 people, and complications such as delayed growth and development from the fetal stage, various physical characteristics, and heart disease are often observed. It is also said that spontaneous miscarriages are 100 times more likely to occur in Patau syndrome than in normal births, reaching approximately 1%.
There is a research report that shows that the probability of having Patau syndrome mosaic is about 5%.The pathology of Patau syndrome with mosaicism is not very clear, but it is thought to tend to be less severe than complete Patau syndrome.
mosaic edwards syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in which there is an extra chromosome 18 is called Edwards syndrome. Edwards syndrome is the second most common chromosomal abnormality after Down syndrome, and it is known to be more common in girls than boys.
The frequency is said to be one in 6,000 to 8,000, but the number of babies born due to abortion or miscarriage is underestimated, so in reality it is one in 2,500 to 2,600. It has been reported that it may be born.
Fetuses with Edwards syndrome have growth problems even before birth, and have abnormalities in their faces and hands. They are also said to have short lifespans because they often have heart and kidney malformations.
Regarding the relationship with mosaic,Less than 5% of people have mosaic chromosome 18There are also reports that show that. A variety of cases have been reported, ranging from cases in which patients with mosaicism die shortly after birth as newborns to cases in which they grow up to be normal adults. Intellectual abilities range from severe mental retardation to above average intelligence. In addition, abnormalities such as microcephaly, delayed bone age, polydactyly, congenital heart defects, developmental delay, short stature, and premature ovarian failure are mostlyLess common than complete Edwards syndromeIt is said that.
However, the relationship between the ratio of normal cells to trisomy cells in the mosaic and clinical symptoms and mental development is not clear. Therefore, research is currently continuing on various counseling issues such as fertility, long-term survival rate, and recurrence risk for individuals with mosaic trisomy 18.
mosaic turner syndrome
I will explain Turner syndrome as an example of mosaic sex chromosomes. Turner syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality in which one of the X chromosomes is missing. It occurs in 1 in 2500 women. Symptoms include short stature and amenorrhea. In addition, because the lymph vessels do not grow properly, there are physical characteristics such as edema of the neck, hands and tops of the feet, which is characteristic of pterygium.
Mosaic type of Turner syndromeOften goes undiagnosedResearch has also shown that. In a UK Biobank study of 244,848 women aged 40 and over, the prevalence of non-mosaic forms 45,X (12/100,000) and 47,XXX (45/100,000) was Although lower than expected, the prevalence of mosaic type 45,X/46,XX (76/100,000 people) was reported to be high. Based on these results, women with mosaic Turner syndromeThere are a certain number of people who go about their daily lives without noticing the symptoms.It is suggested that.
If mosaic is suspected in NIPT
NIPT (New Prenatal Diagnosis)If it is pointed out that there is a chromosomal abnormality,Detailed investigation is required by ultrasound, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus examination.If a test shows that there is a chromosomal abnormality, there is a possibility that there really is a chromosomal abnormality as shown in the test, that there is mosaicism only in the placenta, or that there is mosaicism in the fetus.
NIPT (New Prenatal Diagnosis)This test is currently used as a non-invasive genetic test in Japan.NIPT (New Prenatal Diagnosis)If an abnormality is found, an ultrasound examination or amniocentesis must be performed to confirm the diagnosis in order to obtain information about the fetus inside the womb.
Ultrasound testing is a non-invasive test, but Please understand that amniocentesis and chorionic villus testing are tests that carry the risk of putting stress on the mother and fetus. Also, if you suspect that you have mosaicism, please consult your doctor carefully to find out what risks there are.
Article Editorial Supervisor

Dr. Shun Mizuta
Head Doctor, Hiro Clinic NIPT Okayama
Board Certified Pediatrician, Japan Pediatric Society
As a pediatrician, he has been engaged in community medicine in Okayama Prefecture for nearly 30 years.
Currently, he is working to educate the community about NIPT as the Head Doctor of Hiro Clinic NIPT Okayama, utilizing his experience as a pediatrician.
Brief History
1988 – Graduated from Kawasaki Medical University
1990 – Clinical Assistant, Kawasaki Medical University, Department of Pediatrics
1992 – Department of Pediatric Neurology, Okayama University Hospital
1993 – Head of the First Department of Pediatrics, Ihara Municipal Hospital, Ihara City
1996 – Mizuta Kodomo Hospital
Qualifications
Board Certified Pediatrician
 中文
中文