


For those hearing NIPT for the first time
A blood test alone can be used to test for Down’s syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities in the baby’s tummy.
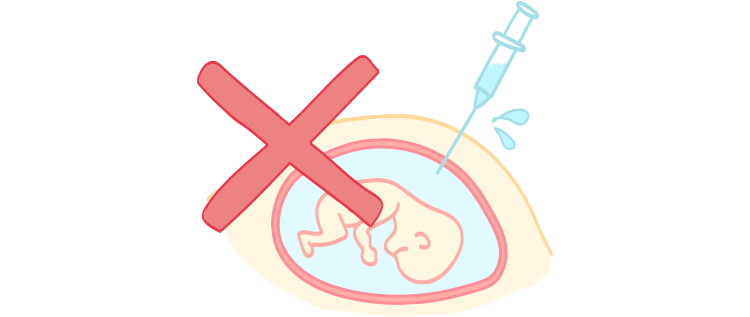
Unlike amniocentesis, no needle is inserted into the abdomen!
※NIPT is a sensitive test but not a definitive test





| Early NIPT | Early Next Generation NIPT | |
|---|---|---|
| Implemented institutions |
General obstetrics and gynecology | Hiro Clinic |
| Target | Basically high risk persons only | Anyone can take the test |
| Number of weeks |
From 10 weeks | After confirmation of pregnancy by echo, from approximately 6 weeks |
| PIC | Counsellor | Doctor |
| Inspection items |
Chromosome 21,18,13 trisomy |
Chromosome 21,18,13 trisomy Sex chromosome aneuploidy Autosomal heterozygosity Partial deletion duplication Microdeletions (4 types) Single-gene diseases (228 types) |
| Amniotic diagnosis |
Referral to mostly university hospitals |
Referral to collaborating clinics Patient’s preferred inspection location (Assisted amniotic fluid support available) |
Down’s Syndrome DNA Check-up
JPY 25,000
JPY 27,500 (incl. tax)
Recommended for those who want to find out about chromosome 21 trisomy (Down syndrome) at a reasonable price.
The quality of the inspection is equivalent to that of the regular inspection plan.
※Report in maximum 15 days.
※ For collaborating clinics, the regular price is JPY 49,500 (incl. tax).
※Not applicable to Early NIPT applicants.
※Only available on weekdays, not available on Saturdays, Sundays and public holidays.
※A separate fee of JPY 25,000 (JPY 27,500 incl. tax) will be charged in case of re-collecting blood due to inability to determine.
※Cancellations and refunds will not be made due to inability to determine.





Premium Plan Hms
JPY 108,800
JPY 119,680 (incl. tax)
A separate fee of JPY 22,000 is charged for use of collaborating clinics.
For Early NIPT, a separate fee of JPY 9,000 (JPY 9,900 incl. tax) is charged. (Limited to 100 people)

Results are delivered within 8 days in 95% of cases from blood collection (except for some plans). When using express delivery, results can be delivered in as little as 2 days. The number of reporting days depends on the desired test.
Hiro Clinic has conducted more than 60,000 examinations of pregnant women. (as of 2025/2).
When NIPT results in a positive result, you will know how positive it really is.

Please enter your zip code. We will find a clinic near you where you can take the NIPT test.
Please include your zip code.
NIPT testing available in your area
You can see the clinic.
NIPT testing available at 125 locations nationwide
search (e.g. for someone using a search engine)
*Available in all prefectures except Okinawa.

Search by Area
NIPT testing at your local clinic
Please do not hesitate to contact us
0120-99-6640
Phone reception hours: 9:00-21:00
Basic Plan O
JPY 99,800
JPY 109,780 (incl. tax)
A separate fee of JPY 22,000 is charged for use of collaborating clinics.
For Early NIPT, a separate fee of JPY 9,000 (JPY 9,900 incl. tax) is charged. (Limited to 100 people)


Q. What if the NIPT tests positive…・
A. Hiro Clinic NIPT offers a post-test consultation with a doctor if desired.(20 minutes JPY 4,000(incl. tax JPY 4,400))
In addition, although NIPT is a highly accurate test, it is not a ‘definitive’ test and it is recommended that an amniotic fluid test is taken to confirm the results.


Q. The cost of having NIPT and further amniotic fluid testing is…
A. Hiro Clinic offers an ‘amniotic fluid test support’ system. Pregnant women with a positive test result are subsidised up to JPY 200,000 (incl. tax) for the cost of an amniotic fluid test. There is no designation of an amniotic fluid testing institute. Amniotic fluid testing can be carried out at a convenient location.


Q. I haven’t heard much about it, except Down’s Syndrome …
A. Other examples include Patou syndrome, which has one extra 13th chromosome, and Edwards syndrome, which has one extra 18th chromosome. The reason is that with the other chromosomes, the chance of being born with the other chromosomes is much lower. Originally, the probability of being born with Down’s syndrome was said to be 1% in the 40s.



Down’s syndrome (21 trisomy) is one of the most frequent genetic disorders in newborns, a chromosomal abnormality that occurs when there is one more chromosome 21 than normal.
Due to an abnormality in the cells called chromosomes, the development of muscles and internal organs is often affected and developmental delays need to be supported at an early stage.
In addition to a characteristic appearance, Down’s syndrome includes delayed intellectual and physical development and complications of other diseases.
Babies with Down’s syndrome have a variety of visual features. The head is small and flattened at the back of the head, the face is broad and flabby, with suspended eyes and a low nose that are particularly noticeable. There is often excess skin on the back of the neck. Ears are small, round and located low on the head.
The fingers of the hand are short and the little finger has only two joints instead of the usual three and is seen bent inwards. There is often only one horizontal crease in the palm of the hand. Fingerprints may occur more frequently in a pattern that runs horizontally instead of in a circle.
They are also generally shorter and at higher risk of obesity.
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) is difficult to generalise as it varies from person to person, but if the IQ of a normal child is 100, the average IQ of a child with Down syndrome is around 50.
Behaviourally, lack of attention, hyperactivity and autistic behaviour (e.g. repeating the same thing over and over) are often observed, as well as a relatively high risk of depression.
About half of all cases of Down’s syndrome are complicated by heart disease. Particularly common are diseases in which the walls dividing the different chambers of the heart are not built up properly (e.g. endocardial floor defects and ventricular septal defects).
Other common complications include gastrointestinal diseases such as duodenal obstruction and cloacal anus, which in some cases may require surgery soon after birth. Complications such as strabismus, deafness and thyroid dysfunction are also common. Weak muscular strength also weakens the ability to swallow, which can lead to problems with drinking milk and eating weaning food.
Although once considered short-lived, today, due to improvements in diagnostic accuracy and medical technology, the average life expectancy in Japan has increased to around 60 years. The main causes of death are heart disease and pneumonia.
The diagnosis of Down’s syndrome is made by confirming the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in a blood test. In the case of a foetus, a maternal amniotic fluid or chorionic villus test is used to test the chromosomes of the foetus. However, amniotic fluid or chorionic villus tests are often performed when screening tests such as ultrasound or NIPT (new-type prenatal diagnosis) indicate the possibility of chromosomal abnormalities, as there is a risk of miscarriage from the tests.
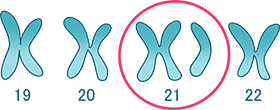
Chromosome 21 contains fewer genes than the other chromosomes
because it contains fewer genes than the other chromosomes,
The chances of being born are higher
than for other diseases.

The incidence of Down’s syndrome is greatly influenced by the age of the mother, with a 1 in 100 at the age of 30, 1 in 1000 at the age of 40, which means that 40-year-olds are ten times more likely to have a child with Down’s syndrome than 30-year-olds.

NIPT testing at your local clinic
Please do not hesitate to contact us
0120-99-6640
Phone reception hours: 9:00-21:00
Medical Corporation Fukubikai
〒332-0017
Hiro Build. 3-11-27 Sakae-cho, Kawaguchi-shi, Saitama.
Hiro Clinic President: Hiroko Oka
Phone number: 0120-16-9629
