The method of calculating Likelihood Ratio (LR) using Short Tandem Repeat (STR) is primarily used in paternity and forensic medicine to test a specific hypothesis (e.g., that a person is the father of a child).
What is Likelihood Ratio (LR)?
The likelihood ratio (LR) is a measure of how likely a given piece of genetic evidence is based on two hypotheses. It is usually calculated based on the following two hypotheses
- Hypothesis 1 (H1): Subject A is the biological father of the child.
- Hypothesis 2 (H2): Subject A is not the biological father of the child and is an unrelated person.
Calculation of likelihood ratios using STR
STR compares the number of repeated sequences (alleles) at a particular locus.In paternity testing, the loci (alleles) of the child are compared to those of the examinee to evaluate the degree of agreement.The likelihood ratio is calculated in the following steps
1. Likelihood calculation for hypothesis 1 (H1)
H1: If respondent A is the father
If respondent A is the father, the probability that the child will inherit a particular allele from the father is 1/2.This is because the probability that the child inherits either one of the father’s two alleles is 1/2.
Likelihood calculation for Hypothesis 2 (H2)
H2: If respondent A is not the father
In this case, the probability that the child’s allele matches an unrelated individual depends on the frequency of that allele in the population. This is estimated from a genetic database, for example, and the frequency of occurrence of that allele in the population (e.g., 0.05) is used.
3. Calculation of likelihood ratio
The likelihood ratio (LR) is calculated as the ratio of the likelihoods of the evidence obtained under the two hypotheses.
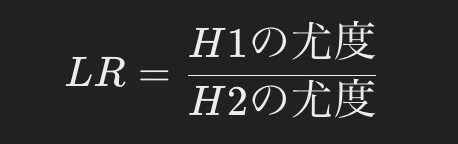
- Likelihood of H1 (if he is the father) = 1/2
- Likelihood of H2 (if not father) = allele frequency (e.g., p)
Thus, LR is calculated as follows
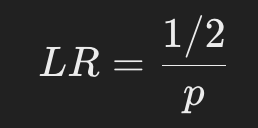
This calculation is performed for each locus and the LRs of all loci are multiplied to obtain the final likelihood ratio.
4. Calculation of LR for multiple loci
STR analysis typically uses multiple loci. For example, LRs are calculated for 13 to 20 loci, and then each LR is multiplied to obtain the overall LR.
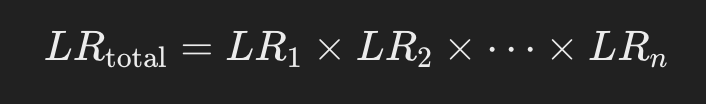
5. Interpretation of LR
- LR greater than 1: Indicates that the hypothesis that respondent A is the father (H1) is more likely than the hypothesis that he is not the father (H2).For example, if LR = 1000, the hypothesis that he is the father is 1000 times more supported than the hypothesis that he is not the father.
- If LR is less than 1: Indicates that the hypothesis that he is not the father (H2) is more likely.
例
Suppose that at a locus, the allele of child and subject A match and the frequency of that allele in the population is 0.05.
- Likelihood of H1 (if he is the father) = 1/2
- Likelihood for H2 (if not father) = 0.05
In this case, the LR is as follows
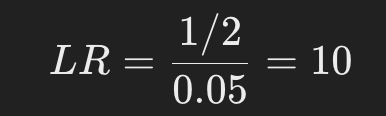
Looking at this locus alone, the probability that respondent A is the father is 10 times higher than the probability that he is not the father.
Summary
- Likelihood ratio (LR) with STR is a method of comparing evidence based on two hypotheses in DNA testing and quantifying which hypothesis is more likely.
- The LR is calculated for each locus and eventually multiplied by the LR of all loci to obtain the overall LR.
- An LR of 1 or greater indicates that the examinee is more likely to be the father, while an LR of less than 1 indicates that the examinee is less likely to be the father.
This method improves the accuracy of parent-child relationship appraisals and personal identification, and allows decisions to be based on scientific evidence.
Here is how to calculate likelihood ratios using SNPs
Latest Articles
Supervisor of the article

Dr. Hiroshi Oka
Graduated from Keio University, Faculty of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine
Medical Doctor









