This section explains how to determine the likelihood ratio (YUDOHI) of a paternity test. Likelihood ratios are particularly important in paternity testing because they indicate how strong a particular hypothesis is compared to other hypotheses.
Likelihood ratios for paternity tests
The likelihood ratio in a paternity test indicates the ratio of the probability that a particular person is the parent to the probability that an unrelated person is the parent. This is sometimes called the Probability Ratio (PR).
Calculation Procedure
Setting up the conflict hypothesis:.
H1: Hypothesis that the examinee is the actual parent.
H2:Hypothesis in which the examinee is an unrelated person.
Selection of genetic markers:.
Typically, STR (short repeat sequence) markers are used. At each marker, the child inherits one gene from each parent.
Alil frequency acquisition:.
To know the frequency of alleles (genetic variants) in each genetic marker, we consult the population database.
Likelihood Calculation:.
Likelihood of H1 (L1): Probability that a child has the observed genotype if the respondent is the parent.
Likelihood of H2 (L2): Probability that a child has the observed genotype if the respondent is an unrelated person.
Calculation of the likelihood ratio:.
Lead Ratio (LR) = L1 / L2
concrete example
Genetic markers and allele frequencies:.
Marker 1: Subject (A1, A2), child (A1, A3), mother (A2, A3)
Frequency of Allyl A1 = p1
Frequency of Allyl A2= p2
Frequency of Allyl A3 = p3
Likelihood Calculation:.
H1(Parents are the test subjects): Assume that the child’s allele A1 was inherited from the father and A3 from the mother.
L1 = 0.5 * 1(Probability of parent-child relationship) = 0.5
H2(Unrelated persons are parents.): Probability that a child’s allele A1 and A3 combination is inherited from an unrelated person.
L2 = 2 * p1 * p3
Calculation of likelihood ratios:.
LR = L1 / L2 = 0.5 / (2 * p1 * p3) = 0.25/(p1*p3)
Combination of multiple markers
If multiple genetic markers are used, the likelihood ratio at each marker is calculated and the product of the likelihood ratios of all markers is taken.
LR_total = LR1 * LR2 * LR3 * … * LRn
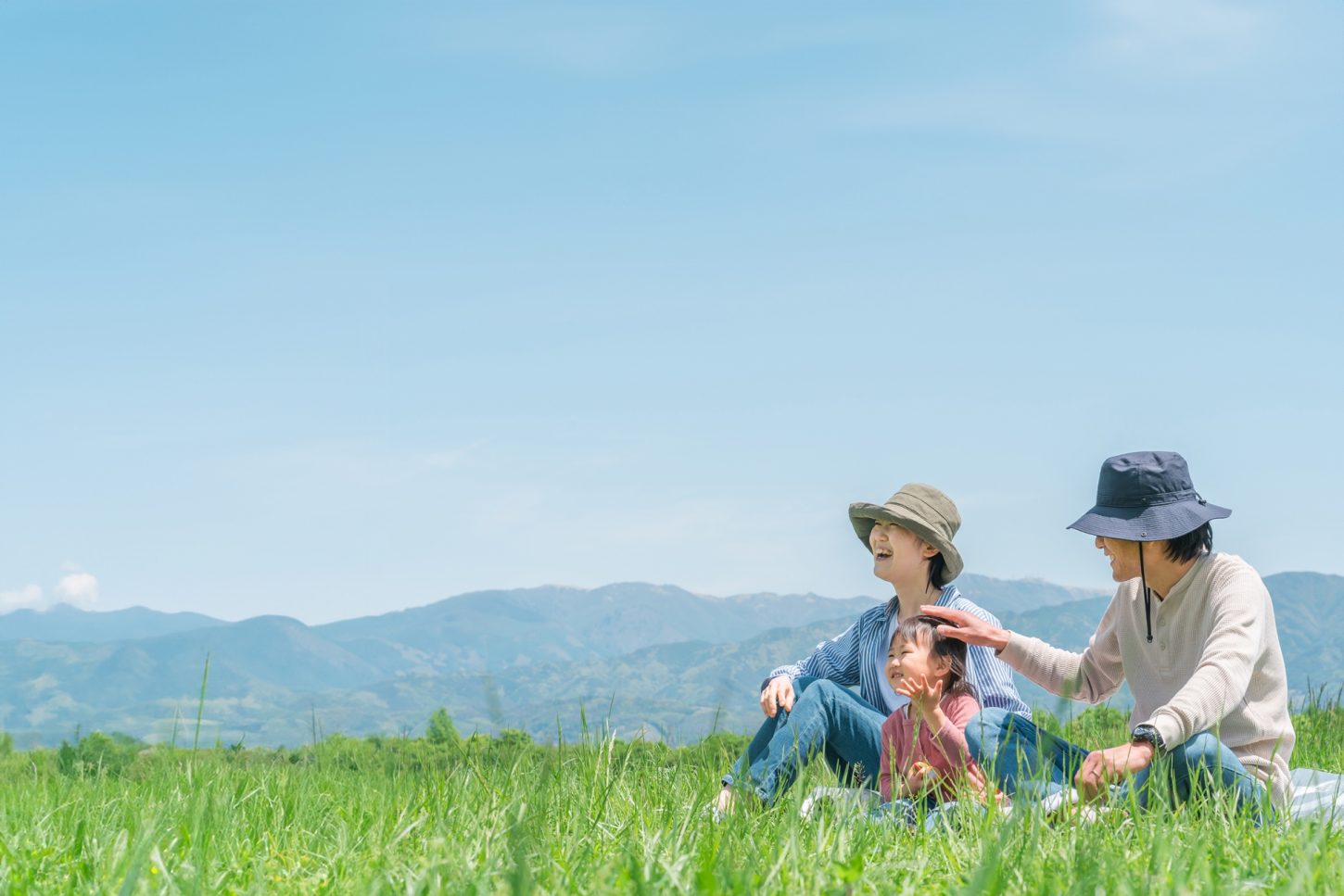
In the case of no match, the likelihood ratio is as follows
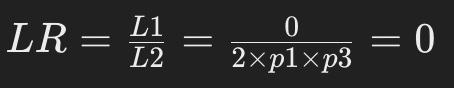
Multiple marker combinations:.
If multiple markers are used, calculate the likelihood ratio for each marker and take the product of the likelihood ratios for all markers.
If there is even one marker that does not match, the likelihood ratio for that marker will be 0.Therefore, the overall likelihood ratio will also be 0.
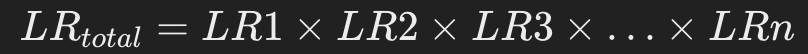
If there is a marker that is not matched, the LR of that marker is 0, so the overall likelihood ratio is also 0.
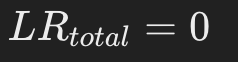
Interpretation of results
A high likelihood ratio (e.g., greater than 1000) strongly supports the hypothesis that the examinee is the parent.
A low likelihood ratio (e.g., less than 1) indicates that the examinee is likely not a parent.
Since the test is performed using STR at HIRO Clinic, the likelihood rate is measured based on the frequency of occurrence of each allele.
Latest Articles
Supervisor of the article

Dr. Hiroshi Oka
Graduated from Keio University, Faculty of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine
Medical Doctor









