Probability of Exclusion (PE) is the probability that if a particular man is not the biological father of a child, DNA testing can accurately determine this.PE is calculated based on the genetic marker used (STR: short chain repeat sequence).
The probability of exclusion is generally found on the basis of the following factors
Frequency of alleles (how common a particular allele is in the population)
Number of loci (number of markers used)Frequency of alleles (how common a particular allele is in the population)
Number of loci (number of markers used)
- Basic formula for calculating the probability of exclusion
- The probability of exclusion (PE) is calculated by assessing the overall evidence for non-paternity at individual loci.PE is usually calculated by accumulating the PEs at individual loci. Basic formula for calculating the probability of exclusion
The probability of exclusion (PE) is calculated by assessing the overall evidence for non-paternity at individual loci.PE is usually calculated by accumulating the PEs at individual loci.
The general PE formula is as follows:
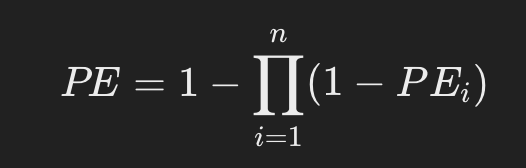
PE_i: Probability of exclusion at each locus (STR marker)
n: Number of loci used (e.g. if there are 20 loci, n = 20)PE_i: Probability of exclusion at each locus (STR marker)
n: Number of loci used (e.g. if there are 20 loci, n = 20)
- Probability of exclusion at each locus (PE_i)
- The probability of exclusion (PE_i) at an individual locus is calculated based on the frequency of alleles at that locus. Specifically, it indicates the probability that the putative father has an allele not inherited from the mother (probability of a non-paternal allele).Probability of exclusion at each locus (PE_i)
The probability of exclusion (PE_i) at an individual locus is calculated based on the frequency of alleles at that locus. Specifically, it indicates the probability that the putative father has an allele not inherited from the mother (probability of a non-paternal allele).
The formula for the probability of exclusion at one locus is as follows:
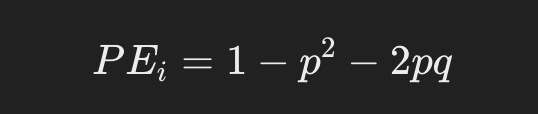
p: frequency of allele A at the locus
q: frequency of allele B at the locus
This calculation depends on whether the alleles are heterozygous (have different alleles) or homozygous (have the same allele) and is based on their respective probabilities. p: frequency of allele A at the locus
q: frequency of allele B at the locus
This calculation depends on whether the alleles are heterozygous (have different alleles) or homozygous (have the same allele) and is based on their respective probabilities.
- Specific examples
- For example, if the frequency of one allele is 0.2 and the frequency of another is 0.3 at a particular locus, it can be calculated as follows: Specific examples
For example, if the frequency of one allele is 0.2 and the frequency of another is 0.3 at a particular locus, it can be calculated as follows:
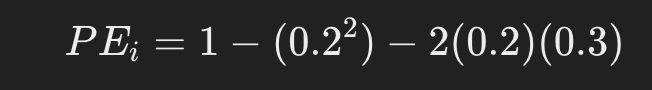
First, calculate the respective values:

This results in a probability of exclusion at a particular locus of 0.84 (84%).
- Overall probability of exclusion
- When determining the probability of exclusion based on several loci, the PEs of each are combined. For example, if there are 20 loci and the probability of exclusion (PE) for each has been calculated, the overall PE is obtained by multiplying all PEs. Overall probability of exclusion
When determining the probability of exclusion based on several loci, the PEs of each are combined. For example, if there are 20 loci and the probability of exclusion (PE) for each has been calculated, the overall PE is obtained by multiplying all PEs.
As an example, assuming that the PEs of the three loci are 0.85, 0.9 and 0.88 respectively, the calculation is as follows:
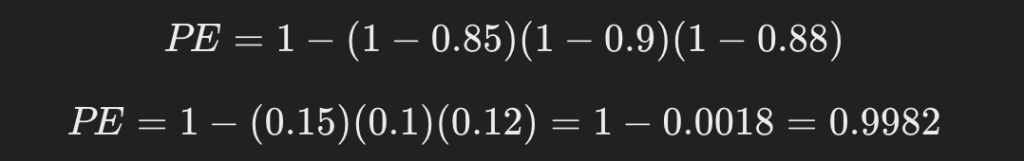
PE=1-(0.15)(0.1)(0.12)=1-0.0018=0.9982
As a result, the overall exclusion probability is 99.82%.
- Conclusions
- The probability of exclusion (PE) is calculated based on the allele frequency per locus, and the more markers used, the higher the overall PE. The final probability of exclusion is calculated by multiplying the probability of exclusion for several loci. The higher this value, the greater the probability that a DNA test will reject paternity. Conclusions
The probability of exclusion (PE) is calculated based on the allele frequency per locus, and the more markers used, the higher the overall PE. The final probability of exclusion is calculated by multiplying the probability of exclusion for several loci. The higher this value, the greater the probability that a DNA test will reject paternity.
Latest Articles
Supervisor of the article

Dr. Hiroshi Oka
Graduated from Keio University, Faculty of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine
Medical Doctor









