The calculation of the probability of paternity negation is used in DNA paternity testing to indicate the likelihood that a father is not the genetic father of a particular child. This includes calculations using Probability of Exclusion (PE) and Paternity Index (PI).
1. Basic concept of paternity negative probability
Paternity denial probability indicates the probability that a particular man is denied the possibility of being the biological father of a child based on the results of a DNA test. This probability is calculated based on the match or mismatch of genetic markers shared between the child and the presumed father.
2. The concept of probability of exclusion (PE)
The probability of exclusion (PE) is the probability that if the presumed father is not the father of the child, this can be detected by DNA testing.PE is determined based on the number of genetic markers used and the likelihood that these markers differ. The more markers and the higher the accuracy, the higher the PE.
3. Calculation of the Paternity Index (PI)
The Paternity Index (PI) quantifies the evidence of paternity at a particular locus; the PI is calculated by comparing the probability of a particular allele being transmitted from father to child with the probability of it being transmitted from an unrelated male unrelated to the mother.
- PI is calculated for each locus (STR: short repeat sequence) and the PI of all loci is multiplied together to give the overall PI.
4. Formula for calculating the probability of paternity denial
The paternity negative probability is calculated using the paternity positive probability (W).
(1) Calculation of paternity affirmation probability
The paternity affirmation probability (W) is calculated by the following equation:
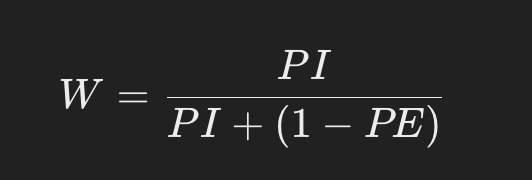
- PI: Overall paternity index.
- PE: Probability of exclusion
(2) Calculation of paternity denial probability
The paternal negative probability is calculated as follows:
Paternal negative probability = 1 – W
That is, the complement of the paternal positive probability is the paternal negative probability. The paternal negative probability is calculated as follows:
Paternal negative probability = 1 – W
That is, the complement of the paternal positive probability is the paternal negative probability.
5. Specific examples
If the overall paternity index (PI) is 1000 and the probability of exclusion (PE) is 0.99 (99%), the paternity affirmation probability is calculated as follows.
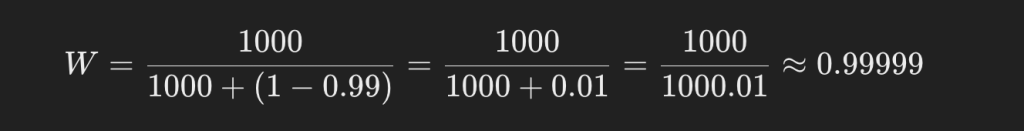
The paternity negative probability is:
1 – 0.99999 = 0.00001 (0.001%)The paternity negative probability is:
1 – 0.99999 = 0.00001 (0.001%)
This means that the paternity negative probability is 0.001%.
6. Use in actual paternity testing
In actual paternity testing, there are many factors that influence the analysis, including the number of genetic markers used and whether maternal DNA is included. Typically, more than 20 STR markers are used to confirm or deny paternity with a high degree of accuracy.
Summary
The calculation of the paternity negative probability is based on the probability of exclusion (PE) and the paternity index (PI).Using these figures, the probability of not being the father is quantified and the final negative probability is obtained.
Latest Articles
Supervisor of the article

Dr. Hiroshi Oka
Graduated from Keio University, Faculty of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine
Medical Doctor









