Introduction: the importance of prenatal parentage testing
Prenatal paternity testing is a DNA test carried out while the fetus is still inside the mother’s body to confirm the parent-child relationship with the potential father. The test uses genetic markers such as STR (Short Tandem Repeat) and SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) to ensure scientific accuracy. In addition, the reliability of the paternity relationship is assessed by calculating the Likelihood Ratio (LR) and Paternity Probability (PP).The Hiro Clinic uses the Likelihood Ratio (LR) and Paternity Probability (PP). At HIRO Clinic, we aim for a level of accuracy where the probability of positive paternity is at least 13 consecutive 9s (99.9999999999999% or higher). This is because this number is larger than the population of the planet, so there is no way that people with identical genes can exist.
A paternity affirmation probability of more than 99.99999999999% indicates that the prospective father is almost certainly the father. This probability is so accurate that it can be regarded as virtually ‘100%’.
Compare this probability with the population of the Earth. The population of the Earth is approximately 8 billion, meaning that a 99.9999999999999% probability means that there is a 0.00000000001% chance (10 minus 11 to the 11th power) that he is not the father. Applying this to the population of the Earth, this corresponds to approximately 0.008 people.
This means that even if all 8 billion people were examined, the probability that he is not the father is very low. This probability is such strong evidence that it is almost certain that a potential father is the father.
Role of STRs and SNPs.
Short Tandem Repeat (STR) refers to regions of the DNA sequence where short sequences are repeated. As the number of these repeats varies from individual to individual, STRs are very useful for confirming parent-child relationships. By comparing the STR patterns of the potential father and the fetus, the presence or absence of a parent-child relationship can be determined with a high degree of accuracy.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP ) refers to the point in DNA where one base is replaced by another SNP is an important indicator of genetic diversity and <a5>more detailed genetic characterisation than STRs can be analysed .Multiple SNPs can be analyzed to further improve the accuracy of confirming parent-child relationships.
Calculation of likelihood ratios (LR)
The likelihood ratio (LR) is the probability that a potential father is actually the father compared to the probability that an unrelated male is the father LR is calculated as follows: the probability that a potential father is the father is calculated as the probability that the potential father is the father of the child:

The higher this value, the more likely it is that the potential father is actually the father. For example, an LR of 1000 is interpreted as meaning that a potential father is 1000 times more likely to be a father than an unrelated male.
Importance of the probability of positive paternity (PP).
Paternity Probability (PP) indicates the probability that a prospective father is actually the father based on LR; PP is calculated as follows: the probability that the prospective father is the father of the child, based on LR, is calculated as: the probability that the prospective father is the father of the child, based on LR:
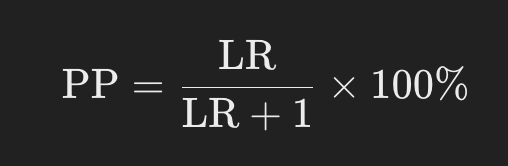
For example, if the LR is 1000, the PP is approximately 99.9%, which means that there is a very high probability that the potential father is the father. PP is an important indicator for confirming parent-child relationships and is also used as legal evidence.
Prenatal paternity testing combining STR with SNPs, LR and PP.
In prenatal paternity testing, multiple STRs and SNPs are usually analyzed and the LRs obtained at each locus are calculated. These LRs are then multiplied together to calculate the overall LR and the final PP. This process ensures the reliability of the appraisal results and is crucial in establishing the parent-child relationship.
For example, if STR analysis determines a 98% agreement on the parent-child relationship, the accuracy can be raised to 99.9% or more by adding SNP analysis. This makes the results of the expert opinion more reliable and makes a significant contribution to establishing legal parent-child relationships and solving social problems.
Implementation and process of prenatal paternity testing.
Prenatal paternity testing is mainly carried out using a non-invasive method of extracting fetal cfDNA (cell-free DNA) from the mother’s blood. cfDNA is present in trace amounts in the mother’s blood, and analysis of this DNA can be analysed to obtain genetic information about the fetus. Non-invasive methods are a very important technique as they can safely confirm parent-child relationships without any risk to the mother or fetus.
Once the fetal DNA has been obtained, genetic analysis is carried out using both STRs and SNPs. Based on the results of the analysis, the LR of each locus is calculated, which is then used to calculate the overall LR and PP. This process allows parent-offspring relationships to be established with a very high degree of accuracy.
Conclusion
Prenatal paternity testing is a very important means of confirming parent-child relationships in utero using advanced genetic analysis techniques combining STRs and SNPs. The results of the appraisal can make a significant contribution to establishing legal parent-child relationships and resolving inheritance and custody issues. The calculation of likelihood ratios and paternity affirmation probabilities ensures the reliability of the appraisals and further increases the accuracy of the results.
Based on the data obtained through STR and SNP analysis, LR and PP can be accurately calculated to provide scientific proof of the parent-child relationship. This process is an integral part of modern parent-child identification and will continue to grow in importance. As science and technology progress, it is hoped that these methods will become more precise and that the confirmation of parent-child relationships will become easier and safer.
Hiro Clinic’s DNA Prenatal Paternity Testing
Hiro Clinic’s DNA Prenatal Paternity Testing (NIPPT) is available at the industry’s lowest price at Hiro Clinic’s directly managed locations nationwide. Testing can be done from the 6th week of pregnancy onward, and the process is completed in a single visit, minimizing inconvenience. If a retest is necessary, it will be conducted free of charge, so you can rest assured. Additionally, tests are conducted at the Tokyo Sanitary Laboratory, which has over 50,000 cases of prenatal testing experience, ensuring reliable results. However, both partners are required to visit the clinic to ensure the most accurate test results. For more information, please check here and make your reservation or inquiry.
Latest Articles
Supervisor of the article

Dr. Hiroshi Oka
Graduated from Keio University, Faculty of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine
Medical Doctor