

Since it’s 40mg, it’s cost-effective to cut it in half or into a quarter for use
What is ED (Erectile Dysfunction)? What are its treatments?
ED (Erectile Dysfunction) refers to a condition in which a man is unable to achieve a normal erection. In Japan, the number of people with severe cases who cannot achieve an erection at all, along with those with moderate cases who experience occasional difficulty, totals approximately 11.3 million. When including mild cases, the number increases even further.
A survey of approximately 2,000 couples found that about 30% reported experiencing ED, indicating that it is a common phenomenon. It is estimated that one in three men suffers from ED, with the incidence increasing with age. Among those aged 60 and older, one in two men struggles with ED.
Previously referred to as “impotence,” the term was changed to “erectile dysfunction” due to its negative connotations. In English, it is commonly abbreviated as ED.
ED refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual activity. Those suffering from this condition may experience an increase in difficulty maintaining an erection or a decrease in erection hardness. It can sometimes be treated with medications for erectile dysfunction.
The important thing to understand is that ED is not something to be ashamed of; rather, it is a common issue. It has also been found that 30% of male infertility cases are caused by erectile dysfunction, making its treatment an essential part of healthcare.
ED is classified into functional and organic types, depending on whether there is an underlying physical problem. Functional ED includes psychogenic and psychiatric causes, while organic ED is categorized into vascular, neurological, endocrine, and penile causes. In some cases, psychological factors and physical disorders overlap. Hiro Clinic provides a comprehensive approach to ED treatment through patient understanding and support.

Causes of ED (Erectile Dysfunction)
ED (Erectile Dysfunction) is a condition that affects both the physical and mental health of men, and its causes are diverse. The term “ED” is an abbreviation for “Erectile Dysfunction” and has become widely recognized in Japan. It is important to understand that ED is not just a localized issue but should be considered as part of a systemic health condition. The main causes of ED include aging, diabetes, obesity and lack of exercise, cardiovascular diseases and hypertension, smoking, decreased testosterone levels, chronic kidney disease and lower urinary tract symptoms, neurological disorders, trauma and surgery, psychological and psychiatric factors, and sleep apnea syndrome. Additionally, ED can sometimes be caused as a side effect of certain medications.
Looking more closely at these causes, aging and lifestyle-related diseases (especially metabolic syndrome) are the primary causes of ED. Patients with cardiovascular disease may experience ED, with data showing that 41.6% of hypertensive patients, 42% of diabetic patients, and 20% of hyperlipidemic patients had ED. ED can also be a precursor to other systemic diseases, making it important to pay attention to its symptoms. An early visit to a urologist is the first step toward appropriate treatment.
【Physical Causes】
①Vascular Disorders: Conditions such as arteriosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes can lead to poor blood circulation, causing ED.
②Neurological Disorders: Spinal cord injuries, diabetic neuropathy, and the effects of surgery or radiation therapy can contribute to ED.
③Hormonal Abnormalities: A decrease in testosterone (male hormone) or endocrine disorders can be a cause of ED.
④Side Effects of Medications: Some medications, including antidepressants and antihypertensive drugs, may cause erectile dysfunction.
⑤Lifestyle-Related Diseases: Obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption are risk factors that can increase the likelihood of ED.

【Psychological Causes】
①Stress: Mental pressure from work, family, or other aspects of life can have an impact.
②Anxiety & Nervousness: Performance anxiety or fear of failure can lead to ED.
③Depression: A depressed state can reduce sexual desire and contribute to ED.
④Relationship Issues: An unstable relationship with a partner can have psychological effects that contribute to ED.

【Others】
①Aging: The risk tends to increase with age, but age alone is not the sole cause.
②Lifestyle: Irregular habits and lack of exercise can affect blood circulation and hormonal balance.

【Mechanism of Erection】
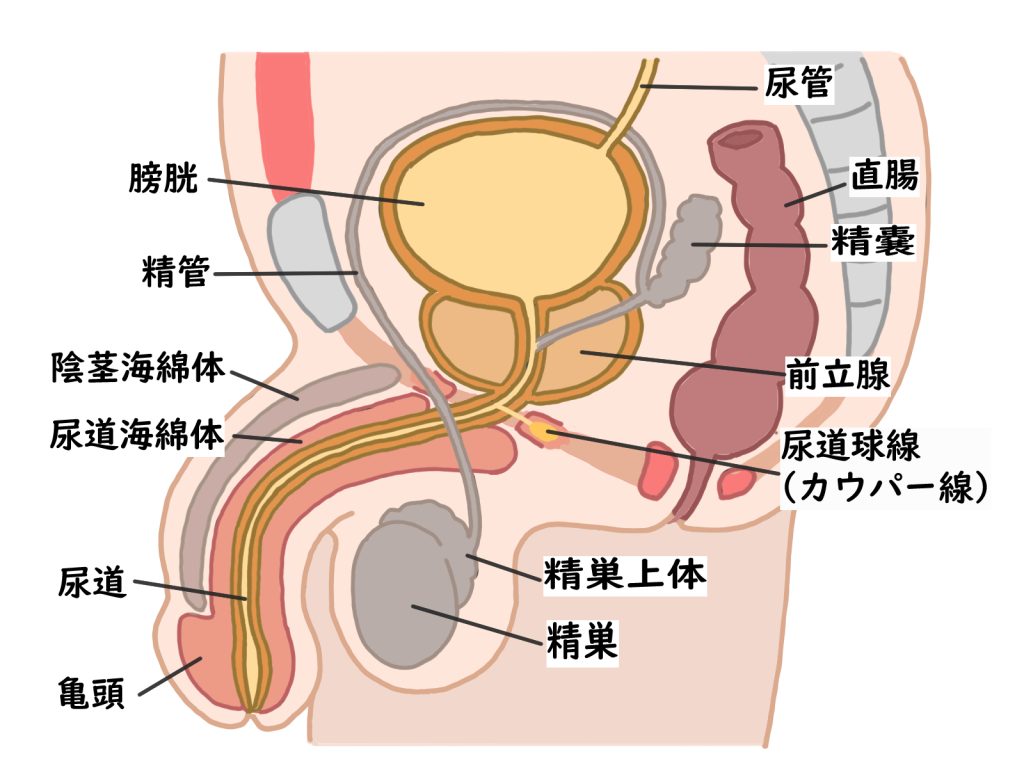
Erection is a complex physiological phenomenon primarily involving two key factors: nerves and blood vessels. When a person experiences sexual stimulation or arousal, the brain sends signals through the nervous system to the penis. This proper functioning of the nervous system initiates the erection process, preparing the blood vessels for the next stage.
During an erection, the blood vessels within the penis expand, allowing a rapid inflow of blood. This influx fills the corpus cavernosum, a spongy tissue inside the penis, causing it to harden and enlarge. The ability to maintain an erection depends on the smooth functioning of these blood vessels, ensuring stable and sustained rigidity. For optimal blood flow, vascular health and flexibility are crucial, and factors such as aging and lifestyle habits can negatively impact blood vessel function, leading to erectile difficulties.
If there is an issue with either the nervous system or blood vessels, a person may experience difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection. For instance, nerve damage can impair the transmission of signals from the brain, reducing responsiveness to stimulation. Similarly, vascular dysfunction may prevent sufficient blood flow, leading to weak or short-lived erections.

【Types of ED】

Organic ED is caused by arteriosclerosis of the blood vessels, which results from aging and lifestyle diseases. Lifestyle diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia accelerate arteriosclerosis and lead to ED. Neurological disorders such as stroke, brain tumors, and spinal cord injuries cause nerve damage, triggering ED. Psychogenic ED occurs when mental stress or trauma interferes with nerve transmission, leading to ED.
Diagnosis of ED (Erectile Dysfunction)
Diagnosis is carefully conducted using tools such as the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF).
The severity of erectile dysfunction (ED) can be classified based on the IIEF score. The IIEF score is based on five domains, with particular emphasis on the “erectile function” domain to assess the severity of ED.
ED Self-Check
ED Self-Check Explanation
The simplified version of the IIEF, called IIEF-5, consists of five questions, each scored from 1 to 5. The total score ranges from 5 to 25, and the severity of ED is classified based on the score.
| 0 Points | 1 Point | 2 Points | 3 Points | 4 Points | 5 Points | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. How confident were you in your ability to maintain an erection? | Very low |
Low |
Normal |
High |
Very high |
|
| 2. How often did you achieve an erection hard enough for penetration with sexual stimulation? | No sexual stimulation |
Almost never or never |
Occasionally (significantly less than half the time) |
Sometimes (about half the time) |
Most of the time (significantly more than half the time) |
Always or almost always |
| 3. How often were you able to maintain an erection after penetration during intercourse? | No sexual stimulation |
Almost never or never |
Occasionally (significantly less than half the time) |
Sometimes (about half the time) |
Most of the time (significantly more than half the time) |
Always or almost always |
| 4. How difficult was it to maintain an erection until the end of intercourse? | No sexual activity |
Extremely difficult |
Very difficult |
Difficult |
Slightly difficult |
Not difficult |
| 5. How often were you satisfied with your sexual performance? | No sexual attempts |
Almost never or never |
Occasionally (significantly less than half the time) |
Sometimes (about half the time) |
Most of the time (significantly more than half the time) |
Always or almost always |
- Severe ED
- Score: 1–7
- The patient is almost or completely unable to maintain an erection.
- Moderate ED
- Score: 8–11
- There is significant difficulty in maintaining an erection, making intercourse often difficult.
- Mild to Moderate ED
- Score: 12–16
- There is some difficulty in maintaining an erection, but intercourse is sometimes possible.
- Mild ED
- Score: 17–21
- There is slight difficulty in maintaining an erection, but intercourse is usually possible.
- No ED
- Score: 22–25
- There are almost no issues with erectile function, and intercourse can be performed normally.

Characteristics of ED (Erectile Dysfunction) Treatment Medications
At Hiro Clinic Urology, we prioritize men’s sexual health and prescribe major ED medications approved by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. In Japan, three medications—Viagra, Levitra, and Cialis—are approved, along with generic drugs containing their active ingredients.
In the past, ED treatment was highly challenging, with limited effective oral treatment options. Treatments such as penile injection therapy, vacuum erection devices, and penile prosthesis implantation were only available at select medical institutions. However, with the introduction of Viagra, ED treatment became more accessible. Today, Viagra, Levitra, Cialis, and their generic equivalents are widely used. These medications generally have an efficacy rate of 70–80%, though individual responses may vary.
| Characteristic | Third Generation Tadalafil (Cialis) | First Generation Sildenafil (Viagra) | Second Generation Vardenafil (Levitra) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Half-life (hours) | Approximately 17.5 hours | Approximately 4–5 hours | Approximately 4–5 hours |
| Duration of effect (hours) | Up to 36 hours | Approximately 4–5 hours | Approximately 4–5 hours |
| Timing of intake | 30 minutes to 1 hour before intercourse | 30 minutes to 1 hour before intercourse | 1 hour before intercourse |
| Effect of food | Minimal effect from food | Easily affected by food (especially high-fat meals) | Easily affected by food (especially high-fat meals) |
| Main indications | ED, Pulmonary Hypertension | ED | ED |
| Main side effects | Headache, indigestion, back pain, muscle pain | Headache, facial flushing, indigestion, visual disturbances | Headache, facial flushing, indigestion, visual disturbances |
Prices of ED (Erectile Dysfunction) Treatment Medications
| Drug Name | Price (Tax Included) | |
|---|---|---|
| Tadalafil 40mg (Cialis) First Trial 1 Tablet |
 |
99 yen/tablet |
| Tadalafil 40mg (Cialis) 1 Tablet |
 |
990 yen/tablet |
| Tadalafil 40mg (Cialis) First Trial 10 Tablet Set |
 |
9,900 yen → Half Price 4,950 yen 495 yen/tablet |
| Tadalafil 40mg (Cialis) 2nd Purchase Onward 10 Tablet Set |
 |
7,920 yen/10 tablets |
| Sildenafil 100mg (Viagra) 1 Tablet |
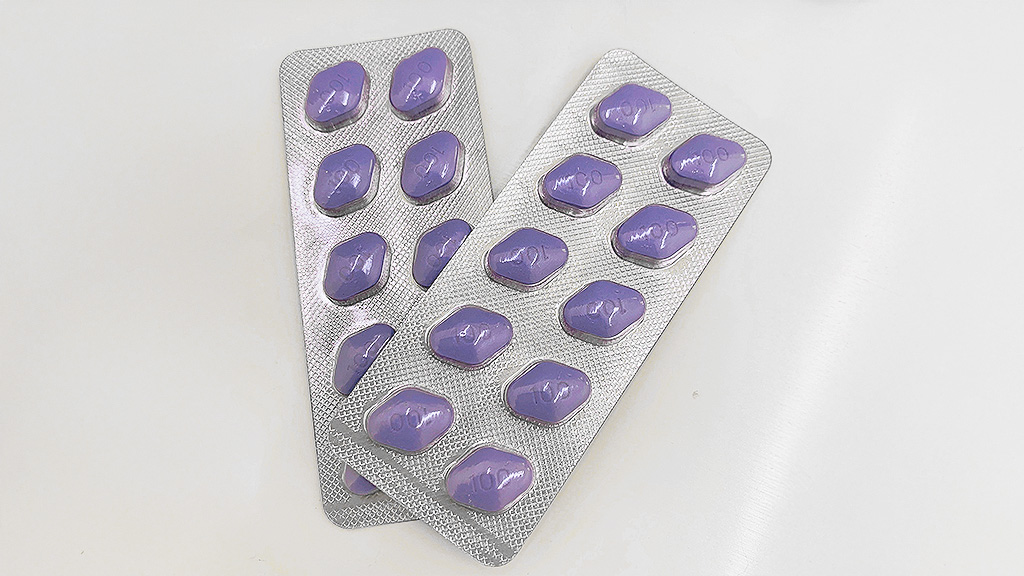 |
990 yen/tablet |
| Sildenafil 100mg (Viagra) NEW First Trial 10 Tablet Set |
 |
9,900 yen → Half Price 4,950 yen 495 yen/tablet |
| Snowvitra Strong 40mg (Levitra) 1 Tablet |
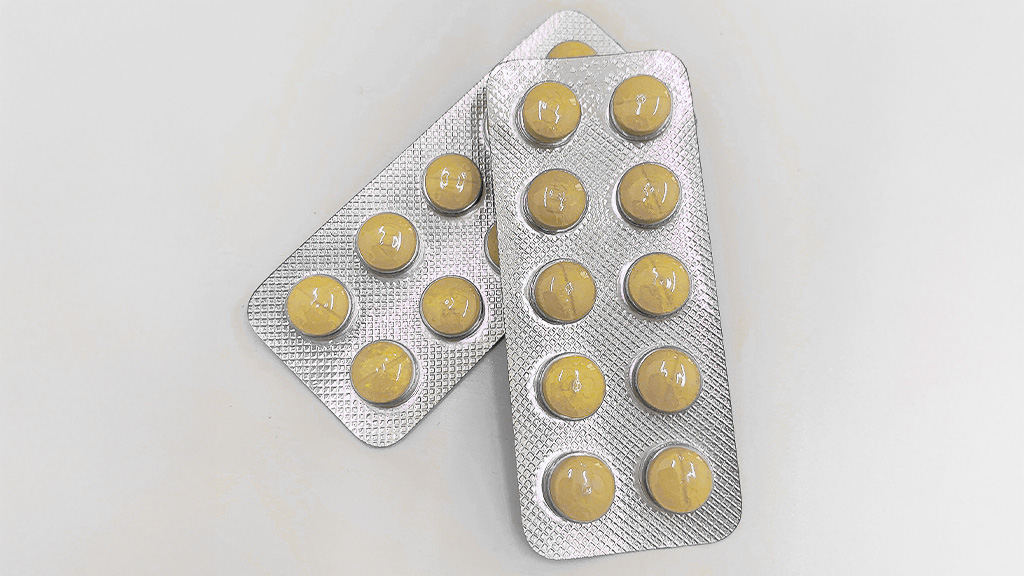 |
990 yen/tablet |
| Snowvitra Strong 40mg (Levitra) First Trial 10 Tablet Set |
 |
9,900 yen → Half Price 4,950 yen 495 yen/tablet |
| Udenafil 100mg | 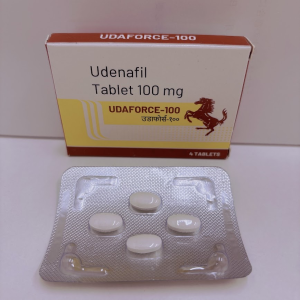 |
5,300 yen/4 tablets (1 sheet) |
| Avanafil 200mg |  |
5,300 yen/4 tablets (1 sheet) |
Japan-made Generic Drug
| Product Name | Selling Price (Tax Included) |
|---|---|
| Sildenafil 50mg “YD” (Viagra) |
2,532 yen/tablet |
| Vardenafil 10mg “Sawai or Towa” (Levitra) |
2,970 yen/tablet |
| Vardenafil 20mg “Sawai or Towa” (Levitra) |
3,300 yen/tablet |
| Tadalafil 20mg “Kracie” | 1,731 yen/tablet |
| Consultation Fee | Free |
|---|
About the Consultation
You can receive medical examinations at Hiro Clinic locations nationwide.
Additionally, we also offer online medical consultations via LINE.
You can make a reservation by phone or through this link.
Online Medical Consultation Process
Register on LINE

Make a Reservation via LINE

At the scheduled time, join via LINE for your online consultation

After the consultation, payment can be made by credit card or bank transfer (cash is also accepted if visiting in person)

After the consultation, we will ship your medication directly to your home

Available for consultations at 14 locations nationwide
For detailed information about clinics nationwide, please see here.
Data Provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
According to data provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is closely related to aging and lifestyle-related diseases, and is recognized as one of the major health issues among men in Japan. As the population ages, the incidence of ED is also increasing, with a particularly strong connection to lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.
Additionally, based on statistics such as the National Health and Nutrition Survey, lifestyle-related diseases are reported as risk factors that increase the likelihood of ED. This data suggests that improving lifestyle habits and appropriate medical interventions are effective in the prevention and treatment of ED.
ED is not merely a physiological issue; it also involves psychological and social impacts, and the number of cases requiring treatment and support is growing. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare is also promoting awareness and treatment of ED.
For detailed data and survey results, you can check the official website of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
On the Insurance Coverage for Pharmaceuticals Used in Infertility Treatment
Information Provided by the Japanese Urological Association
The Japanese Urological Association provides information on Erectile Dysfunction (ED), with particular attention given to the ED treatment guidelines. These guidelines clearly outline the standard process from diagnosis to treatment of ED and serve as a guide for healthcare professionals to provide appropriate treatment. Furthermore, ED risk increases with age, and it is commonly observed in men over the age of 40.
Treatment options related to ED include PDE5 inhibitors (such as Viagra and other pharmacological therapies), psychotherapy, and surgical treatments. The Japanese Urological Association regularly updates research and treatment guidelines related to these methods, providing a wealth of information for healthcare professionals and patients.
For detailed information and guidelines, you can check the official website below.
Japanese Urological Association
ED Treatment Guidelines

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is ED (Erectile Dysfunction)?
- Answer: ED (Erectile Dysfunction) refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual intercourse. ED can occur at any age, and its causes are diverse.
2. What are the main causes of ED?
- Answer: The causes of ED can include psychological factors (such as stress and anxiety), physical factors (such as high blood pressure and diabetes), lifestyle factors (such as smoking and drinking), and side effects from medications. Often, multiple factors are involved. For more details, please check here.
3. Can ED be treated?
- Answer: Yes, ED is treatable in many cases. Treatment options include medications (such as tadalafil or sildenafil), psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. By consulting with a doctor, you can find the treatment that suits you. For more information on treatments, please check here.
4. What are the side effects of ED medications?
- Answer: Common side effects of ED medications include headaches, facial flushing, nasal congestion, indigestion, and changes in vision. Since side effects can vary from person to person, it is important to consult a doctor if you experience concerning symptoms. For more details, please check here.
5. Are ED medications safe?
- Answer: ED medications are considered safe when used as directed by a doctor. However, people with underlying conditions such as cardiovascular disease or those taking certain medications may have restrictions on their use. A doctor’s consultation is required. For more details, please check this page.
6. Can ED be cured by improving lifestyle habits?
- Answer: Yes, improving lifestyle habits can alleviate ED symptoms. Smoking cessation, moderate exercise, a healthy diet, proper sleep, and stress management are considered effective measures.
7. Is ED related to age?
- Answer: The risk of ED increases with age, but young people can also experience ED due to stress or lifestyle factors. Regardless of age, it is advisable to consult a doctor early if symptoms are present.
8. How long does ED treatment take?
- Answer: The duration of treatment depends on the cause and the treatment method. With medication, the effects are often immediate. However, if psychological factors are involved, counseling and additional treatment may be required.
9. Is there a risk of dependency when taking ED medications long-term?
- Answer: Generally, ED medications do not cause physical dependency. However, psychological dependence on the medication may develop, so it is recommended to use them under the guidance of a doctor.
10. Are ED treatments covered by insurance?
- Answer: This varies by country, but ED medications are typically not covered by insurance. However, some treatments and support may be covered by health insurance, so it’s advisable to check with your doctor or insurance provider.





