この記事の概要
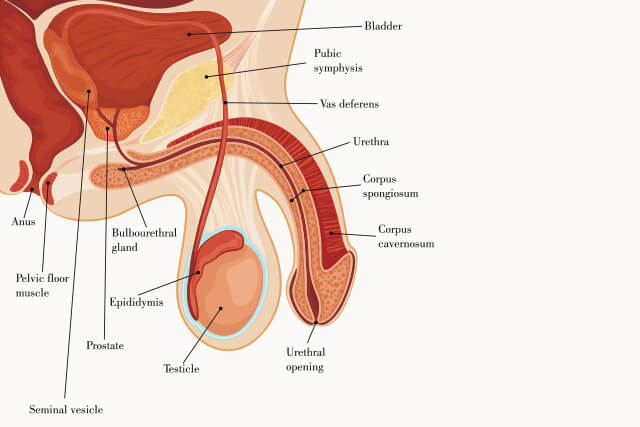
The penis is the passageway for urine and sperm and is an important organ for sexual function.The main structure of the penis consists of three parts
The penis is the passageway for urine and sperm and is an important organ for sexual function. The main structure of the penis consists of three parts

1. Sponge
It consists of the urethral sponge, which runs down the center of the penis, and the penile spongiosa on either side of it.These corpora cavernosa are spongy tissues with numerous cavities, and an erection occurs when these cavities fill with blood upon sexual arousal.
2. Urethra
The urethra is a tube that runs vertically down the center of the penis and is responsible for draining urine and semen from the body. The urethra is protected by the urethral sponge.
3. Foreskin and glans
The glans is located at the tip of the penis and is a very sensory-rich area. The foreskin covers the glans and protects it from stimulation. During sexual arousal, the foreskin retracts to expose the glans.
Relationship to erection (bokki)
An erection is triggered by sexual arousal and occurs when nerve signals from the brain cause the blood vessels in the penis to dilate and blood flows rapidly into the corpus cavernosum. This influx of blood causes the corpus cavernosum to expand and the entire penis to harden. At the same time, the muscles surrounding the corpora cavernosa contract to slow the outflow of blood and maintain the erection.
Erection also causes noticeable changes in the glans.The glans becomes more sensitive and more sexually pleasurable as it expands with blood.
Understanding the structure of the penis and the mechanism of erection is important in maintaining sexual health. When problems such as erectile dysfunction (ED) occur, this knowledge can help identify the cause and select appropriate treatment options.