この記事の概要
Vardenafil (Vardenafil) is a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED).It is known on the market under brand names such as Levitra and Staxyn. The drug works by improving blood flow to support an erection.
Vardenafil (Vardenafil) is a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED).It is known on the market under brand names such as Levitra and Staxyn. These drugs work by improving blood flow to support an erection.

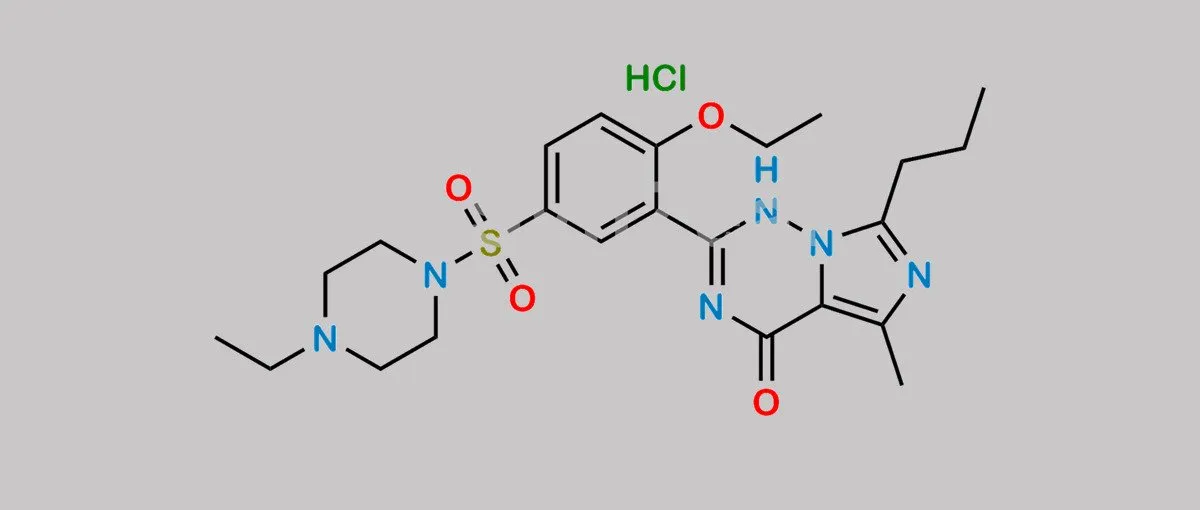
Molecular Structure of Vardenafil
The chemical formula of vardenafil is C23H32N6O4S and has the following structural characteristics
- Triazolopyrimidine ring:.
- The core structure of vardenafil, this heterocyclic portion of the molecule aids in strong binding to PDE5.
- Phenyl group: Phenyl group
- Phenyl groups in the side chains of the molecule increase the liposolubility of the molecule and contribute to the behavior of the drug in the body.
- Ethyl group
- An ethyl group is introduced as part of the molecular structure, which affects the metabolic properties and duration of action of the drug.
- Sulfonamide group
- The sulfonamide portion of the molecule provides water solubility and improves the in vivo solubility and stability of the drug.
Sequence of actions
Vardenafil, like sildenafil and tadalafil, inhibits the activity of the PDE5 enzyme. This enzyme degrades cGMP in penile tissue. cGMP promotes vasodilation and smooth muscle relaxation for erection. Inhibition of PDE5 by vardenafil maintains cGMP levels, allowing for stronger and more sustained erections.
Vardenafil’s molecular structure makes it highly selective for PDE5 and effectively improves the symptoms of ED. Therefore, it can efficiently promote and sustain erections only in the presence of sexual stimulation. It is also often compared to other PDE5 inhibitors in terms of duration of action and side effects, which may be a deciding factor in some patients’ choice.